13th Dec, 2023 13:00
Fine Asian Art Holiday Sale
242
A MONUMENTAL SCHIST FIGURE OF THE GODDESS HARITI, ANCIENT REGION OF GANDHARA
犍陀羅片岩浮雕鬼子母與般闍迦像
Sold for €46,800
including Buyer's Premium
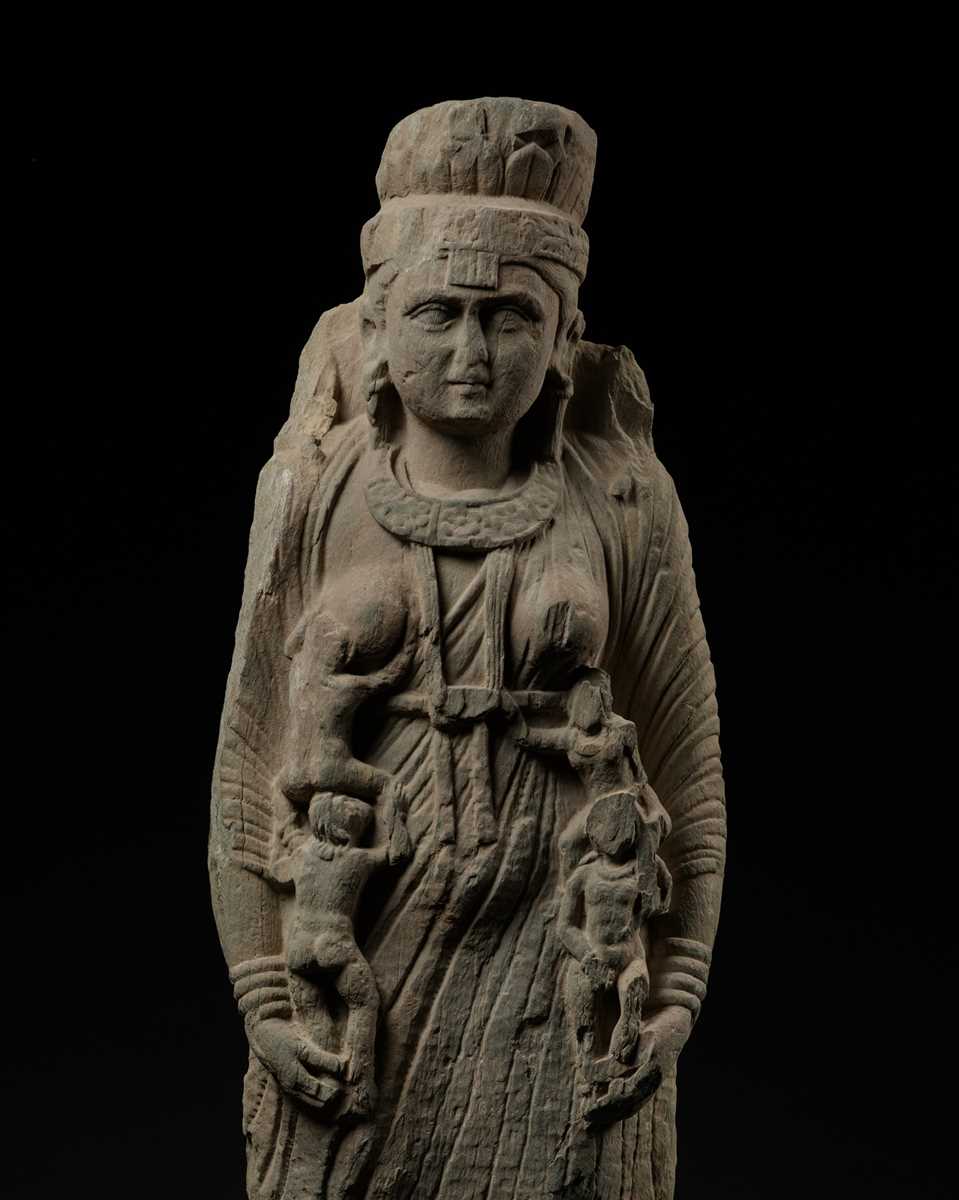
Kushan empire, 2nd-3rd century AD. Wearing a long kaftan, trousers, and a heavily pleated shawl, Hariti’s jewelry is comprised of anklets, rows of bracelets, earrings hanging from her elongated lobes, and necklaces with a large central torque decorated with rosettes. She wears a circular crown topped with a square structure carved with lotus-petal panels in relief above a foliate fillet on top of her finely incised waving hair, and in her two arms she holds four plump nude children, two beneath each breast with one breast covered and the other exposed.
Provenance: Sotheby’s London, 17 October, 1996, sale LN6645, lot 111. Kenneth P. Jackson, United Kingdom, acquired from at the above sale for a hammer price of GBP 50,000, equivalent to a purchase price of GBP 56,500 or EUR 163,000 (converted and adjusted for inflation at the time of writing).
Condition: Condition commensurate with age and presenting remarkably well overall. Expected old wear, weathering and erosion as a result of extensive exposure to the elements across a time period of almost two millennia. Obvious losses, structural cracks, some of which show old fills, remnants of soil encrustations from burial.
Weight: >250 kg
Dimensions: Height 171 cm (excl. base) and 186 cm (incl. base)
Please click here to read the full description
With a modern metal base. (2)
This figure of Hariti, the Buddhist mother goddess, illustrates the unique amalgamation of cross-cultural influences present in ancient Gandhara. It also bears a distinct and early Hellenistic element almost never found in other sculptures from this period and region.
Other figures of Hariti from the High Gandhara period are dressed in heavy robes in the classical manner, like the statue of the seated Hariti in the British Museum, registration number 1886,0611.1 (fig. 1). However, the present lot depicts Hariti in a kaftan, trousers, and a shawl, a concise style of clothing that exemplifies the Scythian influence on the Gandhara people during their rule of the neighboring region of eastern Iran in the 2nd and 3rd centuries AD. The Scythian style of clothing is known in detail from depictions along the palace walls of Apadana (fig. 2) from the Achaemenid period as well as from terracotta figures from the 2nd century AD.
Even more remarkable is the flagrant early Hellenistic influence clearly visible in Hariti’s headdress. The unusual yet characteristic iconography of it links Hariti directly to the Greek goddess Tyche, daughter of Zeus, and suggests she was a rare example of religious syncretism as a direct result of the Hellenistic period in the far east. The headdress of the present Hariti exemplifies this fact unlike most other depictions of the goddess.
Tyche, the goddess of fate, became a prominent figure in the Greek pantheon under Alexander the Great. It was during Alexander’s rule that Tyche came to embody the whims of fate. Her importance within the Greek pantheon is clear and can be seen in sculptures like the colossal head of Tyche next to Zeus and Apollo in Nemrut Dagi (fig. 3).
Tyche’s mural crown (fig. 4) identifies her as the protectorate of cities and links the founding of Sparta to the goddess’s headdress according to S.B. Matheson (see The Goddess Tyche, Yale University Art Gallery Bulletin, 1994). Her iconography changed very little over the centuries during early Roman rule and even later depictions of the goddess in Constantinople’s Hippodrome (fig. 5). The crown of the present Hariti with its two rows resembling lotus petals, is carved upright and straight, much like the walls of Tyche’s fortress headdress. While much of it is worn away, Hariti’s crown is topped by square carvings that closely resemble the crenelated battlement of Tyche’s headdress.
Historians have documented various examples of syncretism between Hellenistic cultures in the Far-East and Buddhism from the 5th century BC to the 4th century AD. This sculpture of Hariti, however, offers an even more unique example of not only cultural syncretism, but also religious syncretism as well. The story of Hariti itself involves the conversion of the goddess to Buddhism. One version of Hariti’s story follows that Hariti had no children. Desperate to have children of her own, the goddess stole children from the locals and raised them as her own. The Buddha, aware of the suffering mothers of the lost children, took back one of the children from Hariti in secret. Amid her grief over the lost child, the Buddha came to her and taught the goddess empathy, showing her the sorrow of mothers from whom she took the children. Hariti subsequently converts to Buddhism, but her foreign origin and nature remains documented by the syncretism seen in the present sculpture.
Literature comparison:
Compare a related Gandharan relief of the goddess Hariti seated and holding a child, 61 cm high, dated 101-300 AD, in the Art Institute of Chicago, reference number 2016.58. Compare a related figure of Hariti with children, 132 cm high, dated to the 2nd century AD, in the Government Museum and Art Gallery, Chandigarh, accession number 1625. Compare a related large schist figure of Hariti with children from the Swat Valley in Gandhara, 125 cm high, dated 2nd-4th century, published by M Akira in Gandharan Art and Bamiyan Site, Tokyo, 2006, pp.114, nr. 86.
Auction result comparison:
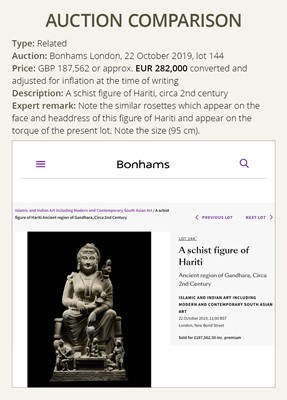
Type: Related
Auction: Bonhams London, 22 October 2019, lot 144
Price: GBP 187,562 or approx. EUR 282,000 converted and adjusted for inflation at the time of writing
Description: A schist figure of Hariti, circa 2nd century
Expert remark: Note the similar rosettes which appear on the face and headdress of this figure of Hariti and appear on the torque of the present lot. Note the size (95 cm).
点此阅读中文翻译 (Chinese Translation)
犍陀羅片岩浮雕鬼子母與般闍迦像
貴霜帝國,西元二至三世紀。鬼子母身著長袍、褲子和披著披肩;佩戴手鐲、耳環,飾有玫瑰花項鍊與叫連,她還戴著一頂圓形葉狀王冠,刻有蓮瓣,波浪捲髮。她雙手抱著四個孩童,胸前還有四個孩子。
來源:倫敦蘇富比1996 年10 月17 日,拍賣LN6645,拍品111;英國Kenneth P. Jackson在上述拍賣中以50,000 英鎊的落槌價購得,相當於購買價56,500 英鎊或163,000 歐元(換算後的價格,在撰寫本文時已根據通貨膨脹進行了調整)。
品相:狀況良好。有磨損、風化和侵蝕,明顯的缺損、結構裂縫,其中一些有填充物、埋藏時土壤結殼的殘留物。
重量:250 公斤
尺寸:高 171 厘米 (不含底座) 與 186 厘米 (含底座)
現代金屬支架. (2)
文獻比較:
比較一件相近的西元101-300年犍陀羅鬼子母與般闍迦浮雕像,高61 厘米,收藏於芝加哥藝術博物館,館藏編號2016.58。比較一件相近的二世紀鬼子母與般闍迦像,132 厘米 高,收藏於昌迪加爾政府博物館和美術館,館藏編號1625。比較一件相近的二至四世紀犍陀羅斯瓦特谷鬼子母與般闍迦像,高125 厘米,出版於Akira,《Gandharan Art and Bamiyan Site》,東京,2006年,頁114,編號86。
拍賣比較:
形制:相近
拍賣:倫敦邦翰斯,2019年10月22日,lot 144
價格:GBP 187,562(相當今日EUR 282,000)
描述:約二世紀片岩浮雕鬼子母與般闍迦像
專家註釋:請注意類似的玫瑰花結出現在鬼子母的臉部和頭飾上。請注意 尺寸 (95 厘米)。
Kushan empire, 2nd-3rd century AD. Wearing a long kaftan, trousers, and a heavily pleated shawl, Hariti’s jewelry is comprised of anklets, rows of bracelets, earrings hanging from her elongated lobes, and necklaces with a large central torque decorated with rosettes. She wears a circular crown topped with a square structure carved with lotus-petal panels in relief above a foliate fillet on top of her finely incised waving hair, and in her two arms she holds four plump nude children, two beneath each breast with one breast covered and the other exposed.
Provenance: Sotheby’s London, 17 October, 1996, sale LN6645, lot 111. Kenneth P. Jackson, United Kingdom, acquired from at the above sale for a hammer price of GBP 50,000, equivalent to a purchase price of GBP 56,500 or EUR 163,000 (converted and adjusted for inflation at the time of writing).
Condition: Condition commensurate with age and presenting remarkably well overall. Expected old wear, weathering and erosion as a result of extensive exposure to the elements across a time period of almost two millennia. Obvious losses, structural cracks, some of which show old fills, remnants of soil encrustations from burial.
Weight: >250 kg
Dimensions: Height 171 cm (excl. base) and 186 cm (incl. base)
Please click here to read the full description
With a modern metal base. (2)
This figure of Hariti, the Buddhist mother goddess, illustrates the unique amalgamation of cross-cultural influences present in ancient Gandhara. It also bears a distinct and early Hellenistic element almost never found in other sculptures from this period and region.
Other figures of Hariti from the High Gandhara period are dressed in heavy robes in the classical manner, like the statue of the seated Hariti in the British Museum, registration number 1886,0611.1 (fig. 1). However, the present lot depicts Hariti in a kaftan, trousers, and a shawl, a concise style of clothing that exemplifies the Scythian influence on the Gandhara people during their rule of the neighboring region of eastern Iran in the 2nd and 3rd centuries AD. The Scythian style of clothing is known in detail from depictions along the palace walls of Apadana (fig. 2) from the Achaemenid period as well as from terracotta figures from the 2nd century AD.
Even more remarkable is the flagrant early Hellenistic influence clearly visible in Hariti’s headdress. The unusual yet characteristic iconography of it links Hariti directly to the Greek goddess Tyche, daughter of Zeus, and suggests she was a rare example of religious syncretism as a direct result of the Hellenistic period in the far east. The headdress of the present Hariti exemplifies this fact unlike most other depictions of the goddess.
Tyche, the goddess of fate, became a prominent figure in the Greek pantheon under Alexander the Great. It was during Alexander’s rule that Tyche came to embody the whims of fate. Her importance within the Greek pantheon is clear and can be seen in sculptures like the colossal head of Tyche next to Zeus and Apollo in Nemrut Dagi (fig. 3).
Tyche’s mural crown (fig. 4) identifies her as the protectorate of cities and links the founding of Sparta to the goddess’s headdress according to S.B. Matheson (see The Goddess Tyche, Yale University Art Gallery Bulletin, 1994). Her iconography changed very little over the centuries during early Roman rule and even later depictions of the goddess in Constantinople’s Hippodrome (fig. 5). The crown of the present Hariti with its two rows resembling lotus petals, is carved upright and straight, much like the walls of Tyche’s fortress headdress. While much of it is worn away, Hariti’s crown is topped by square carvings that closely resemble the crenelated battlement of Tyche’s headdress.
Historians have documented various examples of syncretism between Hellenistic cultures in the Far-East and Buddhism from the 5th century BC to the 4th century AD. This sculpture of Hariti, however, offers an even more unique example of not only cultural syncretism, but also religious syncretism as well. The story of Hariti itself involves the conversion of the goddess to Buddhism. One version of Hariti’s story follows that Hariti had no children. Desperate to have children of her own, the goddess stole children from the locals and raised them as her own. The Buddha, aware of the suffering mothers of the lost children, took back one of the children from Hariti in secret. Amid her grief over the lost child, the Buddha came to her and taught the goddess empathy, showing her the sorrow of mothers from whom she took the children. Hariti subsequently converts to Buddhism, but her foreign origin and nature remains documented by the syncretism seen in the present sculpture.
Literature comparison:
Compare a related Gandharan relief of the goddess Hariti seated and holding a child, 61 cm high, dated 101-300 AD, in the Art Institute of Chicago, reference number 2016.58. Compare a related figure of Hariti with children, 132 cm high, dated to the 2nd century AD, in the Government Museum and Art Gallery, Chandigarh, accession number 1625. Compare a related large schist figure of Hariti with children from the Swat Valley in Gandhara, 125 cm high, dated 2nd-4th century, published by M Akira in Gandharan Art and Bamiyan Site, Tokyo, 2006, pp.114, nr. 86.
Auction result comparison:
Type: Related
Auction: Bonhams London, 22 October 2019, lot 144
Price: GBP 187,562 or approx. EUR 282,000 converted and adjusted for inflation at the time of writing
Description: A schist figure of Hariti, circa 2nd century
Expert remark: Note the similar rosettes which appear on the face and headdress of this figure of Hariti and appear on the torque of the present lot. Note the size (95 cm).
点此阅读中文翻译 (Chinese Translation)
犍陀羅片岩浮雕鬼子母與般闍迦像
貴霜帝國,西元二至三世紀。鬼子母身著長袍、褲子和披著披肩;佩戴手鐲、耳環,飾有玫瑰花項鍊與叫連,她還戴著一頂圓形葉狀王冠,刻有蓮瓣,波浪捲髮。她雙手抱著四個孩童,胸前還有四個孩子。
來源:倫敦蘇富比1996 年10 月17 日,拍賣LN6645,拍品111;英國Kenneth P. Jackson在上述拍賣中以50,000 英鎊的落槌價購得,相當於購買價56,500 英鎊或163,000 歐元(換算後的價格,在撰寫本文時已根據通貨膨脹進行了調整)。
品相:狀況良好。有磨損、風化和侵蝕,明顯的缺損、結構裂縫,其中一些有填充物、埋藏時土壤結殼的殘留物。
重量:250 公斤
尺寸:高 171 厘米 (不含底座) 與 186 厘米 (含底座)
現代金屬支架. (2)
文獻比較:
比較一件相近的西元101-300年犍陀羅鬼子母與般闍迦浮雕像,高61 厘米,收藏於芝加哥藝術博物館,館藏編號2016.58。比較一件相近的二世紀鬼子母與般闍迦像,132 厘米 高,收藏於昌迪加爾政府博物館和美術館,館藏編號1625。比較一件相近的二至四世紀犍陀羅斯瓦特谷鬼子母與般闍迦像,高125 厘米,出版於Akira,《Gandharan Art and Bamiyan Site》,東京,2006年,頁114,編號86。
拍賣比較:
形制:相近
拍賣:倫敦邦翰斯,2019年10月22日,lot 144
價格:GBP 187,562(相當今日EUR 282,000)
描述:約二世紀片岩浮雕鬼子母與般闍迦像
專家註釋:請注意類似的玫瑰花結出現在鬼子母的臉部和頭飾上。請注意 尺寸 (95 厘米)。
Zacke Live Online Bidding
Our online bidding platform makes it easier than ever to bid in our auctions! When you bid through our website, you can take advantage of our premium buyer's terms without incurring any additional online bidding surcharges.
To bid live online, you'll need to create an online account. Once your account is created and your identity is verified, you can register to bid in an auction up to 12 hours before the auction begins.
Intended Spend and Bid Limits
When you register to bid in an online auction, you will need to share your intended maximum spending budget for the auction. We will then review your intended spend and set a bid limit for you. Once you have pre-registered for a live online auction, you can see your intended spend and bid limit by going to 'Account Settings' and clicking on 'Live Bidding Registrations'.
Your bid limit will be the maximum amount you can bid during the auction. Your bid limit is for the hammer price and is not affected by the buyer’s premium and VAT. For example, if you have a bid limit of €1,000 and place two winning bids for €300 and €200, then you will only be able to bid €500 for the rest of the auction. If you try to place a bid that is higher than €500, you will not be able to do so.
Online Absentee and Telephone Bids
You can now leave absentee and telephone bids on our website!
Absentee Bidding
Once you've created an account and your identity is verified, you can leave your absentee bid directly on the lot page. We will contact you when your bids have been confirmed.
Telephone Bidding
Once you've created an account and your identity is verified, you can leave telephone bids online. We will contact you when your bids have been confirmed.
Classic Absentee and Telephone Bidding Form
You can still submit absentee and telephone bids by email or fax if you prefer. Simply fill out the Absentee Bidding/Telephone bidding form and return it to us by email at office@zacke.at or by fax at +43 (1) 532 04 52 20. You can download the PDF from our Upcoming Auctions page.
How-To Guides
How to Create Your Personal Zacke Account
How to Register to Bid on Zacke Live
How to Leave Absentee Bids Online
How to Leave Telephone Bids Online
中文版本的操作指南
创建新账号
注册Zacke Live在线直播竞拍(免平台费)
缺席投标和电话投标
Third-Party Bidding
We partner with best-in-class third-party partners to make it easy for you to bid online in the channel of your choice. Please note that if you bid with one of our third-party online partners, then there will be a live bidding surcharge on top of your final purchase price. You can find all of our fees here. Here's a full list of our third-party partners:
- 51 Bid Live
- EpaiLive
- ArtFoxLive
- Invaluable
- LiveAuctioneers
- the-saleroom
- lot-tissimo
- Drouot
Please note that we place different auctions on different platforms. For example, in general, we only place Chinese art auctions on 51 Bid Live.
Bidding in Person
You must register to bid in person and will be assigned a paddle at the auction. Please contact us at office@zacke.at or +43 (1) 532 04 52 for the latest local health and safety guidelines.