6th Mar, 2021 10:00
TWO-DAY AUCTION - Fine Chinese Art / 中國藝術集珍 / Buddhism & Hinduism
614
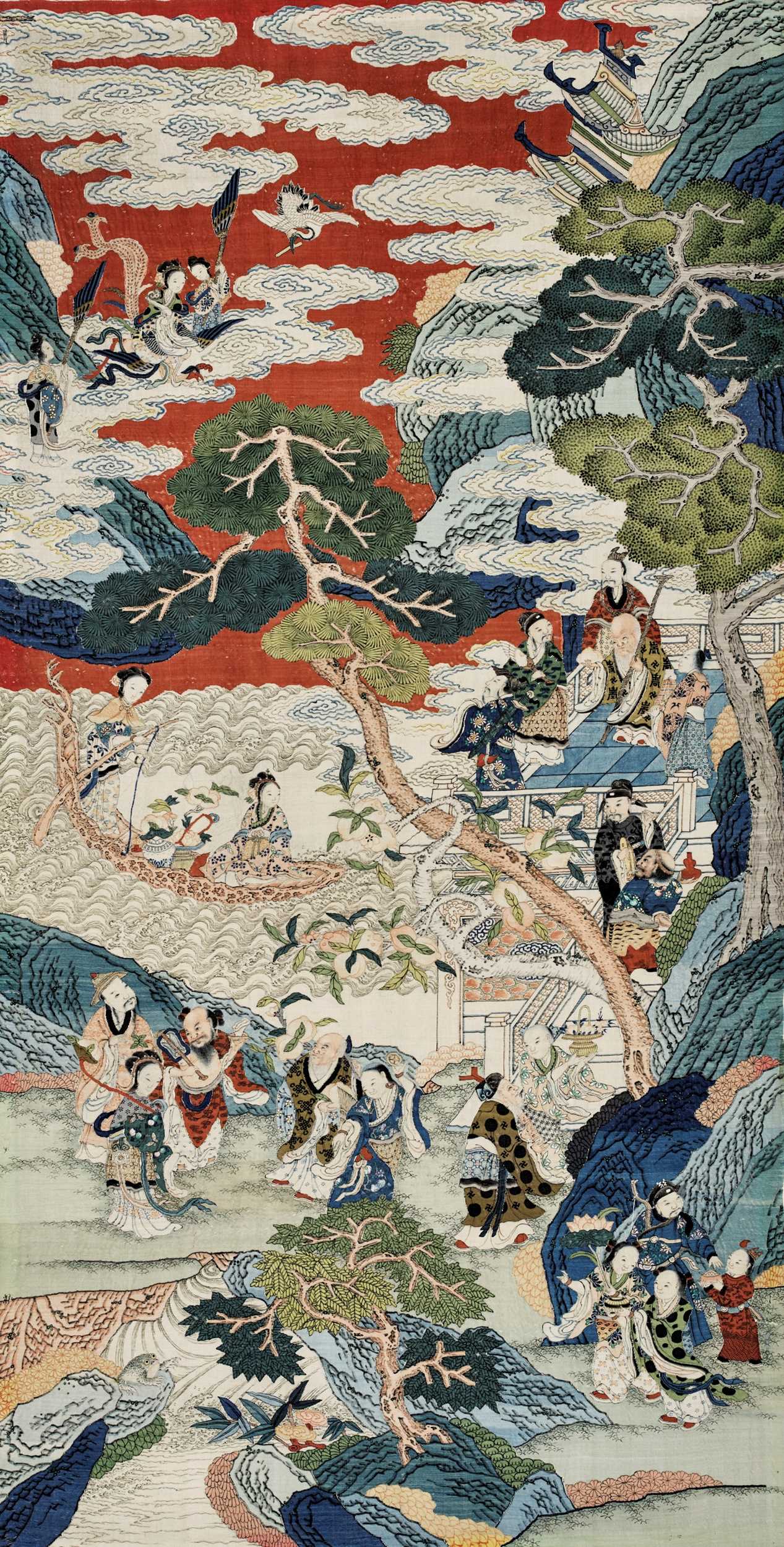
AN IMPORTANT AND LARGE KESI ‘PEACH FESTIVAL’ PANEL, QING DYNASTY
清代重要緙絲《蟠桃宴》壁挂
Sold for €27,808
including Buyer's Premium
China, 1644-1912. Richly embroidered in bright colors with a lively scene depicting the legendary festival, with Xiwangmu, the Queen Mother of the West, descending from the sky astride her phoenix, flanked by two attendants, a crane in flight above. A pantheon of Daoist immortals and deities, including Shoulao, the Eight Immortals, Lui Hai, and Hehe Erxian, all holding ruyi-scepters, eagerly await her arrival on a garden terrace with lingzhi, pine and peach trees issuing from craggy rockwork.
Provenance: From an old British private collection, by repute formed in the first half of the 20th century.
Condition: Pristine condition with very bright and fresh colors, few loose threads to edges, very little minor soiling, and minimal tiny losses. Laid down on paper.
Dimensions: Size 175 x 89 cm
Expert’s note: Large kesi panels depicting this subject or variations thereof commonly appear on the auction market, most with irrevocably faded colors and manifold other condition issues. The present panel is arguably the best-preserved example on the market in a very long time: The colors are virtually as fresh as new, the embroidery is extremely detailed, and the iridescent luster of the silk is almost hypnotic. Most likely it has been rolled up ever since it was mounted on paper, and therefore was never exposed to light before.
The Peach Festival is a popular Daoist theme associated with the birthday celebration of Xiwangmu, who has the sole authority to grant Peaches of Eternal Life and bestow celebrants of the festival with great fortune. According to legend, the festival is held at the Jade Palace in the Kunlun Mountains in the Western paradise and only takes place every 3000 years. Here, groups of Immortals are pictured waiting in anticipation for Xiwangmu, who gracefully arrives on a phoenix. The auspicious message of this theme made the present panel suitable for presentation at important festivities.
Kesi, which means ‘cut silk’, derives from the visual illusion of cut threads that is created by distinct, unblended areas of color, as the weft threads are woven into each color and then cut. The earliest surviving examples of kesi tapestries date to the Tang dynasty (618-907), although the technique was already used earlier in wool and became widely used only during the Song dynasty (1127-1379). The fragment of a kesi tapestry has been recovered in a tomb of a man and his wife in Dulan, Qinghai province, who died in 633 and 688 respectively, and another also excavated in Dulan, was included in the exhibition “China, Dawn of a Golden Age” at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, 2005, cat. no. 245.
During the Ming dynasty (1368-1644), kesi panels enjoyed a rise in popularity and thrived under the Qing emperors. Early in the Qing dynasty (1644-1911) official weaving workshops were established both in the Palace and in the cities of Jiangning, Suzhou and Hangzhou, in order to cater to the Court’s increasing demand for palace and temple furnishings, clothing and presentation silks for civil and military officials. Specialized centers of production soon developed around this area, such as the city of Wenzhou, Zhenjiang province, which became particularly famous for its luxurious kesi tapestries.
Literature comparison: A closely related silk kesi panel with a similar bright red sky in the collection of the Palace Museum, Beijing, is illustrated in Zhongguo Meishu Quanji - Gongyi Meishu Bian, vol. 7, Beijing, 1987, pl. 180, where it is dated to the Qing Dynasty. A slightly larger kesi panel depicting the Peach Festival, from the Liaoning Provincial Museum, Shenyang, was included in the Hong Kong Oriental Ceramic Society exhibition Heaven’s Embroidered Cloths, One Thousand Years of Chinese Textiles, Hong Kong Museum of Art, Hong Kong, 1995, cat. no. 119. Compare also a kesi panel depicting Xiwangmu being greeted by female Immortals in the National Palace Museum, Taipei, included in the exhibition Masterpieces of Chinese Silk Tapestry and Embroidery in the National Palace Museum, Taipei, 1998, cat. no. 21.
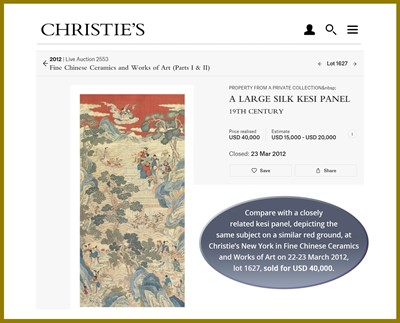
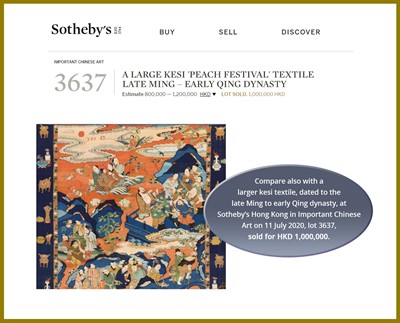
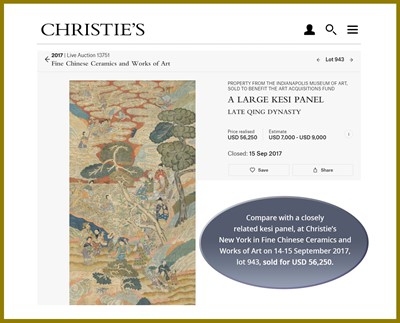
Auction result comparison: Compare with a closely related kesi panel, depicting the same subject on a similar red ground, at Christie’s New York in Fine Chinese Ceramics and Works of Art on 22-23 March 2012, lot 1627, sold for USD 40,000, and another at Christie’s New York in Fine Chinese Ceramics and Works of Art on 14-15 September 2017, lot 943, sold for USD 56,250. Compare also with a larger kesi textile, dated to the late Ming to early Qing dynasty, at Sotheby’s Hong Kong in Important Chinese Art on 11 July 2020, lot 3637, sold for HKD 1,000,000.
清代重要緙絲《蟠桃宴》壁挂
中國,1644-1912年。絲綫鮮艷,生動地描繪了傳說中的蟠桃盛會。西王母騎在鳳凰上從天而降,兩側是侍從,頭上仙鶴飛舞。壽老、八仙、劉海以及和合二仙都在露臺上急切地等待著西王母的到來,四周可見靈芝、松樹和桃花樹。
來源:英國私人老收藏,據説購於二十世紀上半葉。
品相:原始狀態,色彩依然非常鮮豔,邊緣絲綫輕微鬆動,輕微污漬,缺損極小,裱在紙上。
尺寸:175 x 89 厘米
專家注釋: 描繪此主題的大型緙絲壁挂出現在拍賣市場上的,大多數帶有不可避免的褪色和其他各種問題。當前的壁挂可以說是很長一段時間以來市場上保存最完好的:顏色幾乎與新的一樣新鮮,刺繡非常細緻。 自從將其裝裱在紙上以來,很可能是將其捲起,因此以前從未暴露在日光下。
緙絲,又稱刻絲,是中國傳統的一種絲織品,其特色是以緙織方式織造,緯線並不橫貫全幅,而僅在需要處與經線交織。尚存的最早的緙絲壁挂實例可追溯到唐朝(618-907),開始將此技法用於絲織品。南宋時期緙絲得到廣泛使用。緙絲壁挂曾在青海省都蘭墳墓中被發現。在紐約大都會博物館2005年的展覽“China, Dawn of a Golden Age” 也曾展出過另一塊出土緙絲,目錄圖 245。
在明朝(1368-1644),緙絲壁挂受歡迎程度不斷提高,並在清朝皇帝的統治下蓬勃發展。 清朝初期(1644-1911年),在皇宮以及江寧、蘇州和杭州等城市都建立了官方的織布作坊,以滿足宮廷和廟宇陳設、服裝和文職和軍事官員所用絲綢的日益增長的需求。很快就出現了特殊的生產中心,例如浙江溫州,以其豪華的緙絲掛毯而聞名。
文獻比較: 一件清代相近紅地緙絲見北京故宮博物院見《中國美術全集》,工藝美術編,第 7冊, 北京, 1987年, 圖 180. 一件《蟠桃會》大型緙絲見遼寧省博物館的展品,見香港美術館 Hong Kong Oriental Ceramic Society exhibition Heaven’s Embroidered Cloths, One Thousand Years of Chinese Textiles, 1995年,圖119。還有一件西王母緙絲見臺北故宮博物院Masterpieces of Chinese Silk Tapestry and Embroidery 展覽, 1998, 圖 21.
拍賣結果比較:一件相似紅地緙絲壁挂售于紐約佳士得Fine Chinese Ceramics and Works of Art 拍場2012年3月 22-23日 lot 1627, 售價USD 40,000, 另一件售于紐約佳士得Fine Chinese Ceramics and Works of Art 拍場2017年9月14-15日 lot 943, 售價USD 56,250。 還有一件明末清初緙絲見香港蘇富比Important Chinese Art拍場2020年7月11日 lot 3637, 售價HKD 1,000,000。
China, 1644-1912. Richly embroidered in bright colors with a lively scene depicting the legendary festival, with Xiwangmu, the Queen Mother of the West, descending from the sky astride her phoenix, flanked by two attendants, a crane in flight above. A pantheon of Daoist immortals and deities, including Shoulao, the Eight Immortals, Lui Hai, and Hehe Erxian, all holding ruyi-scepters, eagerly await her arrival on a garden terrace with lingzhi, pine and peach trees issuing from craggy rockwork.
Provenance: From an old British private collection, by repute formed in the first half of the 20th century.
Condition: Pristine condition with very bright and fresh colors, few loose threads to edges, very little minor soiling, and minimal tiny losses. Laid down on paper.
Dimensions: Size 175 x 89 cm
Expert’s note: Large kesi panels depicting this subject or variations thereof commonly appear on the auction market, most with irrevocably faded colors and manifold other condition issues. The present panel is arguably the best-preserved example on the market in a very long time: The colors are virtually as fresh as new, the embroidery is extremely detailed, and the iridescent luster of the silk is almost hypnotic. Most likely it has been rolled up ever since it was mounted on paper, and therefore was never exposed to light before.
The Peach Festival is a popular Daoist theme associated with the birthday celebration of Xiwangmu, who has the sole authority to grant Peaches of Eternal Life and bestow celebrants of the festival with great fortune. According to legend, the festival is held at the Jade Palace in the Kunlun Mountains in the Western paradise and only takes place every 3000 years. Here, groups of Immortals are pictured waiting in anticipation for Xiwangmu, who gracefully arrives on a phoenix. The auspicious message of this theme made the present panel suitable for presentation at important festivities.
Kesi, which means ‘cut silk’, derives from the visual illusion of cut threads that is created by distinct, unblended areas of color, as the weft threads are woven into each color and then cut. The earliest surviving examples of kesi tapestries date to the Tang dynasty (618-907), although the technique was already used earlier in wool and became widely used only during the Song dynasty (1127-1379). The fragment of a kesi tapestry has been recovered in a tomb of a man and his wife in Dulan, Qinghai province, who died in 633 and 688 respectively, and another also excavated in Dulan, was included in the exhibition “China, Dawn of a Golden Age” at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, 2005, cat. no. 245.
During the Ming dynasty (1368-1644), kesi panels enjoyed a rise in popularity and thrived under the Qing emperors. Early in the Qing dynasty (1644-1911) official weaving workshops were established both in the Palace and in the cities of Jiangning, Suzhou and Hangzhou, in order to cater to the Court’s increasing demand for palace and temple furnishings, clothing and presentation silks for civil and military officials. Specialized centers of production soon developed around this area, such as the city of Wenzhou, Zhenjiang province, which became particularly famous for its luxurious kesi tapestries.
Literature comparison: A closely related silk kesi panel with a similar bright red sky in the collection of the Palace Museum, Beijing, is illustrated in Zhongguo Meishu Quanji - Gongyi Meishu Bian, vol. 7, Beijing, 1987, pl. 180, where it is dated to the Qing Dynasty. A slightly larger kesi panel depicting the Peach Festival, from the Liaoning Provincial Museum, Shenyang, was included in the Hong Kong Oriental Ceramic Society exhibition Heaven’s Embroidered Cloths, One Thousand Years of Chinese Textiles, Hong Kong Museum of Art, Hong Kong, 1995, cat. no. 119. Compare also a kesi panel depicting Xiwangmu being greeted by female Immortals in the National Palace Museum, Taipei, included in the exhibition Masterpieces of Chinese Silk Tapestry and Embroidery in the National Palace Museum, Taipei, 1998, cat. no. 21.
Auction result comparison: Compare with a closely related kesi panel, depicting the same subject on a similar red ground, at Christie’s New York in Fine Chinese Ceramics and Works of Art on 22-23 March 2012, lot 1627, sold for USD 40,000, and another at Christie’s New York in Fine Chinese Ceramics and Works of Art on 14-15 September 2017, lot 943, sold for USD 56,250. Compare also with a larger kesi textile, dated to the late Ming to early Qing dynasty, at Sotheby’s Hong Kong in Important Chinese Art on 11 July 2020, lot 3637, sold for HKD 1,000,000.
清代重要緙絲《蟠桃宴》壁挂
中國,1644-1912年。絲綫鮮艷,生動地描繪了傳說中的蟠桃盛會。西王母騎在鳳凰上從天而降,兩側是侍從,頭上仙鶴飛舞。壽老、八仙、劉海以及和合二仙都在露臺上急切地等待著西王母的到來,四周可見靈芝、松樹和桃花樹。
來源:英國私人老收藏,據説購於二十世紀上半葉。
品相:原始狀態,色彩依然非常鮮豔,邊緣絲綫輕微鬆動,輕微污漬,缺損極小,裱在紙上。
尺寸:175 x 89 厘米
專家注釋: 描繪此主題的大型緙絲壁挂出現在拍賣市場上的,大多數帶有不可避免的褪色和其他各種問題。當前的壁挂可以說是很長一段時間以來市場上保存最完好的:顏色幾乎與新的一樣新鮮,刺繡非常細緻。 自從將其裝裱在紙上以來,很可能是將其捲起,因此以前從未暴露在日光下。
緙絲,又稱刻絲,是中國傳統的一種絲織品,其特色是以緙織方式織造,緯線並不橫貫全幅,而僅在需要處與經線交織。尚存的最早的緙絲壁挂實例可追溯到唐朝(618-907),開始將此技法用於絲織品。南宋時期緙絲得到廣泛使用。緙絲壁挂曾在青海省都蘭墳墓中被發現。在紐約大都會博物館2005年的展覽“China, Dawn of a Golden Age” 也曾展出過另一塊出土緙絲,目錄圖 245。
在明朝(1368-1644),緙絲壁挂受歡迎程度不斷提高,並在清朝皇帝的統治下蓬勃發展。 清朝初期(1644-1911年),在皇宮以及江寧、蘇州和杭州等城市都建立了官方的織布作坊,以滿足宮廷和廟宇陳設、服裝和文職和軍事官員所用絲綢的日益增長的需求。很快就出現了特殊的生產中心,例如浙江溫州,以其豪華的緙絲掛毯而聞名。
文獻比較: 一件清代相近紅地緙絲見北京故宮博物院見《中國美術全集》,工藝美術編,第 7冊, 北京, 1987年, 圖 180. 一件《蟠桃會》大型緙絲見遼寧省博物館的展品,見香港美術館 Hong Kong Oriental Ceramic Society exhibition Heaven’s Embroidered Cloths, One Thousand Years of Chinese Textiles, 1995年,圖119。還有一件西王母緙絲見臺北故宮博物院Masterpieces of Chinese Silk Tapestry and Embroidery 展覽, 1998, 圖 21.
拍賣結果比較:一件相似紅地緙絲壁挂售于紐約佳士得Fine Chinese Ceramics and Works of Art 拍場2012年3月 22-23日 lot 1627, 售價USD 40,000, 另一件售于紐約佳士得Fine Chinese Ceramics and Works of Art 拍場2017年9月14-15日 lot 943, 售價USD 56,250。 還有一件明末清初緙絲見香港蘇富比Important Chinese Art拍場2020年7月11日 lot 3637, 售價HKD 1,000,000。
Zacke Live Online Bidding
Our online bidding platform makes it easier than ever to bid in our auctions! When you bid through our website, you can take advantage of our premium buyer's terms without incurring any additional online bidding surcharges.
To bid live online, you'll need to create an online account. Once your account is created and your identity is verified, you can register to bid in an auction up to 12 hours before the auction begins.
Intended Spend and Bid Limits
When you register to bid in an online auction, you will need to share your intended maximum spending budget for the auction. We will then review your intended spend and set a bid limit for you. Once you have pre-registered for a live online auction, you can see your intended spend and bid limit by going to 'Account Settings' and clicking on 'Live Bidding Registrations'.
Your bid limit will be the maximum amount you can bid during the auction. Your bid limit is for the hammer price and is not affected by the buyer’s premium and VAT. For example, if you have a bid limit of €1,000 and place two winning bids for €300 and €200, then you will only be able to bid €500 for the rest of the auction. If you try to place a bid that is higher than €500, you will not be able to do so.
Online Absentee and Telephone Bids
You can now leave absentee and telephone bids on our website!
Absentee Bidding
Once you've created an account and your identity is verified, you can leave your absentee bid directly on the lot page. We will contact you when your bids have been confirmed.
Telephone Bidding
Once you've created an account and your identity is verified, you can leave telephone bids online. We will contact you when your bids have been confirmed.
Classic Absentee and Telephone Bidding Form
You can still submit absentee and telephone bids by email or fax if you prefer. Simply fill out the Absentee Bidding/Telephone bidding form and return it to us by email at office@zacke.at or by fax at +43 (1) 532 04 52 20. You can download the PDF from our Upcoming Auctions page.
How-To Guides
How to Create Your Personal Zacke Account
How to Register to Bid on Zacke Live
How to Leave Absentee Bids Online
How to Leave Telephone Bids Online
中文版本的操作指南
创建新账号
注册Zacke Live在线直播竞拍(免平台费)
缺席投标和电话投标
Third-Party Bidding
We partner with best-in-class third-party partners to make it easy for you to bid online in the channel of your choice. Please note that if you bid with one of our third-party online partners, then there will be a live bidding surcharge on top of your final purchase price. You can find all of our fees here. Here's a full list of our third-party partners:
- 51 Bid Live
- EpaiLive
- ArtFoxLive
- Invaluable
- LiveAuctioneers
- the-saleroom
- lot-tissimo
- Drouot
Please note that we place different auctions on different platforms. For example, in general, we only place Chinese art auctions on 51 Bid Live.
Bidding in Person
You must register to bid in person and will be assigned a paddle at the auction. Please contact us at office@zacke.at or +43 (1) 532 04 52 for the latest local health and safety guidelines.