29th Sep, 2022 13:00
DAY 1 - TWO-DAY AUCTION - Fine Chinese Art / 中國藝術集珍 / Buddhism & Hinduism
225
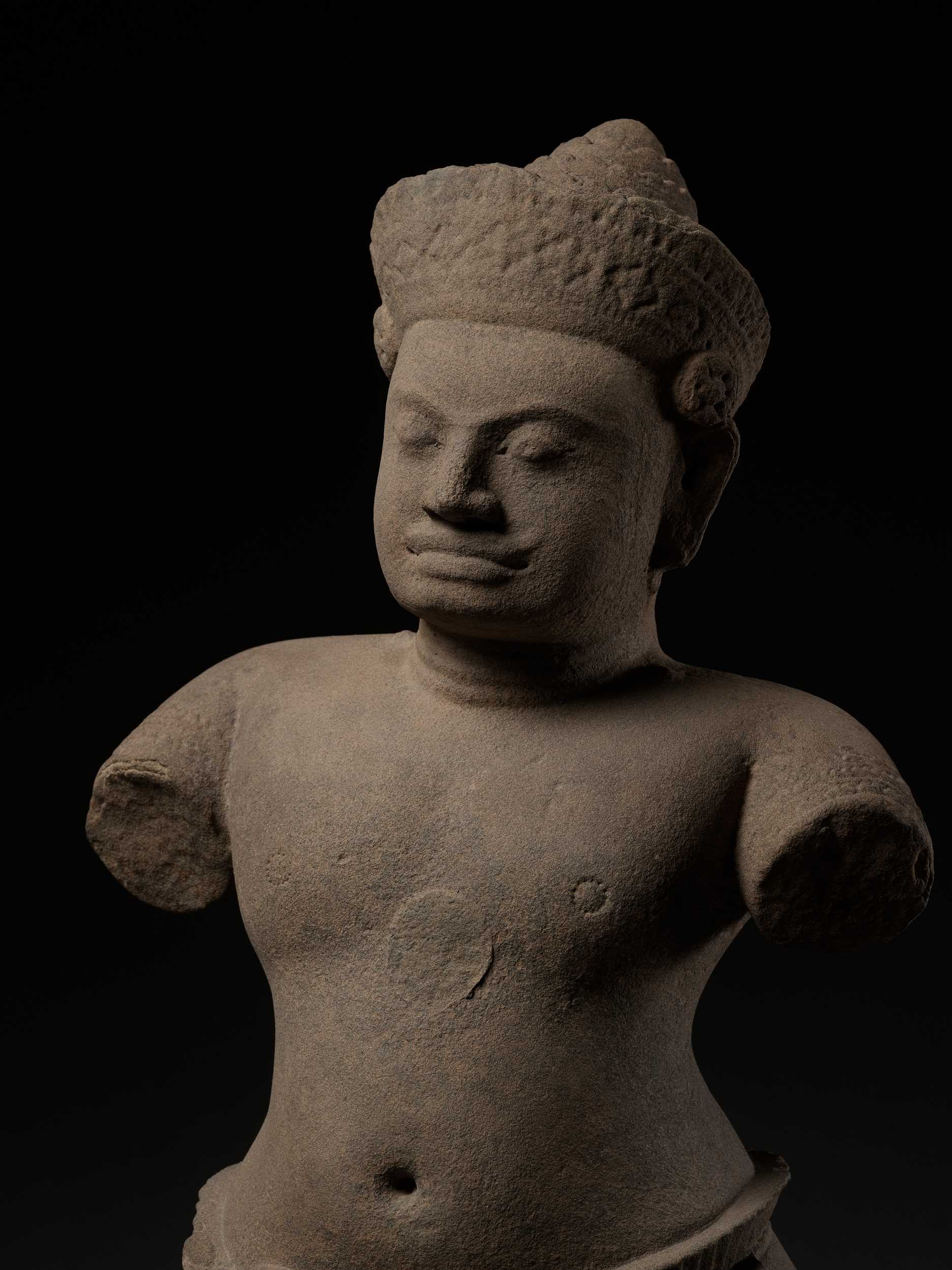
† A SANDSTONE FIGURE OF A DVARAPALA, KOH KER STYLE, ANGKOR PERIOD
Sold for €10,480
including Buyer's Premium
Khmer Empire, early 10th century. Superbly carved, standing in a wide-legged dancing stance, his back slightly arched and his legs strong and taut. His chest is full, his right shoulder is slightly raised and in keeping with the preferred style of the period, he is stoutly built with a rounded stomach. The position of the upper arms suggests that his hands were placed in namaskara mudra (respectfully greeting) in front of his body and the disc shape on the chest marks an area originally covered by the two thumbs. His head is tilted slightly to the left side, his expression is serene and distinctly confident, given further emphasis by his full lips and broad smile, the hair drawn into a conical chignon secured with a foliate tiara.
Provenance: From a notable collector in London, United Kingdom.
Condition: Excellent condition, commensurate with age. Extensive wear, some nicks, losses, minor signs of weathering and erosion, few structural cracks.
Dimensions: Height 72 cm (excl. stand) and 78 cm (incl. stand)
The dvarapala wears a short garment with a curving upper edge that adds emphasis to the massive strength of his body. The fine pleats and delicate curve at the edge of the fabric seem to defy the nature of the stone. A long scarf falls between the legs and would originally have extended to the ankles. Its sway further indicates the sense of movement contained within the figure.
Mounted on an associated metal stand. (2)
A dvarapala is a temple guardian. In India, where the concept originated, two giant figures, sculpted in high relief, are often found flanking the principal temple entrance. One is formidable, to scare away those of ill intent while the other is seductively handsome, in order to lure the faithful past the portal. In Cambodia the form evolved separately because the temples were built to different plans. There, a succession of courtyards contained secondary buildings and the principal one was only accessible to a limited number of ritual participants. In the 10th century dvarapala were freestanding statues, still sculpted in pairs but resting within the precinct. Although they observed approaching visitors, their essential role was that of bodyguards, protecting the deity lodged within the temple.
This latter role appears to have become increasingly dominant in the Koh Ker period when the supremacy of the kings of Angkor was challenged by a powerful royal claimant who established another court to the north of the Kulen mountains, from where he imposed martial rule on much of the kingdom. The achievement of this alternative court is reflected in some of the finest works of art to emanate from Cambodia during the Angkor period. The sculptures are notable for their spontaneous appearance, strong personalities and sense of inner, spiritual energy. Even when the subject is not a recognizable deity, the suggestion of individual personality is always present. This image of a dvarapala exemplifies the style of the period, full of confident swagger but maintaining a deeply serious purpose in his guardian role.
Benign dvarapalas can often be found flanking doorways or protruding from corner brackets, while apsaras are ubiquitous to the temples of Angkor. Dvarapalas became integral to temple sculpture in India as early as the 5th century and appear in Cambodia in the earliest of the Angkor Empire's temples, the Roulos group, constructed around the turn of the 10th century. The Shaivite temples at Koh Ker are similar to these in their iconographical programs and architectural structures.
Koh Ker, which lies 50 miles (80 km) northeast of Angkor, was the capital of the Khmer Empire from 928-944. Koh Ker's sculptural style is thus distinct from those developed in Angkor's immediate vicinity. The stone sculpture, often monumental in size, is imbued with a heightened sense of movement and a suppleness of form.
Expert’s note: A detailed commentary on the present lot, elaborating on the history and architecture of the Khmer Empire, the Koh Ker style, and the sculpture itself and showing many further comparisons to examples in both public and private collections, is available upon request. To receive a PDF of this academic dossier, please refer to the department.
Literature comparison:
Compare two closely related larger Koh Ker sandstone figures, 236 cm and 234 cm high, in the collection of the National Museum of Cambodia, inventory numbers NMC.149 and NMC.150. Compare a related Koh Ker sandstone figure of a female dancing deity in the Musée Guimet, illustrated by Helen Jessup and Thierry Zephir in Sculpture of Angkor and Ancient Cambodia: Millennium of Glory, Paris, 1997, cat. no. 43.
Auction result comparison:
Type: Related
Auction: Christie’s New York, 20 March 2009, lot 1428
Price: USD 146,500 or approx. EUR 198,000 converted and adjusted for inflation at the time of writing
Description: A monumental gray sandstone figure of a Dvarapala, Khmer, Koh Ker Style, 10th century
Expert remark: Note the significantly larger size (129.5 cm)
Khmer Empire, early 10th century. Superbly carved, standing in a wide-legged dancing stance, his back slightly arched and his legs strong and taut. His chest is full, his right shoulder is slightly raised and in keeping with the preferred style of the period, he is stoutly built with a rounded stomach. The position of the upper arms suggests that his hands were placed in namaskara mudra (respectfully greeting) in front of his body and the disc shape on the chest marks an area originally covered by the two thumbs. His head is tilted slightly to the left side, his expression is serene and distinctly confident, given further emphasis by his full lips and broad smile, the hair drawn into a conical chignon secured with a foliate tiara.
Provenance: From a notable collector in London, United Kingdom.
Condition: Excellent condition, commensurate with age. Extensive wear, some nicks, losses, minor signs of weathering and erosion, few structural cracks.
Dimensions: Height 72 cm (excl. stand) and 78 cm (incl. stand)
The dvarapala wears a short garment with a curving upper edge that adds emphasis to the massive strength of his body. The fine pleats and delicate curve at the edge of the fabric seem to defy the nature of the stone. A long scarf falls between the legs and would originally have extended to the ankles. Its sway further indicates the sense of movement contained within the figure.
Mounted on an associated metal stand. (2)
A dvarapala is a temple guardian. In India, where the concept originated, two giant figures, sculpted in high relief, are often found flanking the principal temple entrance. One is formidable, to scare away those of ill intent while the other is seductively handsome, in order to lure the faithful past the portal. In Cambodia the form evolved separately because the temples were built to different plans. There, a succession of courtyards contained secondary buildings and the principal one was only accessible to a limited number of ritual participants. In the 10th century dvarapala were freestanding statues, still sculpted in pairs but resting within the precinct. Although they observed approaching visitors, their essential role was that of bodyguards, protecting the deity lodged within the temple.
This latter role appears to have become increasingly dominant in the Koh Ker period when the supremacy of the kings of Angkor was challenged by a powerful royal claimant who established another court to the north of the Kulen mountains, from where he imposed martial rule on much of the kingdom. The achievement of this alternative court is reflected in some of the finest works of art to emanate from Cambodia during the Angkor period. The sculptures are notable for their spontaneous appearance, strong personalities and sense of inner, spiritual energy. Even when the subject is not a recognizable deity, the suggestion of individual personality is always present. This image of a dvarapala exemplifies the style of the period, full of confident swagger but maintaining a deeply serious purpose in his guardian role.
Benign dvarapalas can often be found flanking doorways or protruding from corner brackets, while apsaras are ubiquitous to the temples of Angkor. Dvarapalas became integral to temple sculpture in India as early as the 5th century and appear in Cambodia in the earliest of the Angkor Empire's temples, the Roulos group, constructed around the turn of the 10th century. The Shaivite temples at Koh Ker are similar to these in their iconographical programs and architectural structures.
Koh Ker, which lies 50 miles (80 km) northeast of Angkor, was the capital of the Khmer Empire from 928-944. Koh Ker's sculptural style is thus distinct from those developed in Angkor's immediate vicinity. The stone sculpture, often monumental in size, is imbued with a heightened sense of movement and a suppleness of form.
Expert’s note: A detailed commentary on the present lot, elaborating on the history and architecture of the Khmer Empire, the Koh Ker style, and the sculpture itself and showing many further comparisons to examples in both public and private collections, is available upon request. To receive a PDF of this academic dossier, please refer to the department.
Literature comparison:
Compare two closely related larger Koh Ker sandstone figures, 236 cm and 234 cm high, in the collection of the National Museum of Cambodia, inventory numbers NMC.149 and NMC.150. Compare a related Koh Ker sandstone figure of a female dancing deity in the Musée Guimet, illustrated by Helen Jessup and Thierry Zephir in Sculpture of Angkor and Ancient Cambodia: Millennium of Glory, Paris, 1997, cat. no. 43.
Auction result comparison:
Type: Related
Auction: Christie’s New York, 20 March 2009, lot 1428
Price: USD 146,500 or approx. EUR 198,000 converted and adjusted for inflation at the time of writing
Description: A monumental gray sandstone figure of a Dvarapala, Khmer, Koh Ker Style, 10th century
Expert remark: Note the significantly larger size (129.5 cm)
Zacke Live Online Bidding
Our online bidding platform makes it easier than ever to bid in our auctions! When you bid through our website, you can take advantage of our premium buyer's terms without incurring any additional online bidding surcharges.
To bid live online, you'll need to create an online account. Once your account is created and your identity is verified, you can register to bid in an auction up to 12 hours before the auction begins.
Intended Spend and Bid Limits
When you register to bid in an online auction, you will need to share your intended maximum spending budget for the auction. We will then review your intended spend and set a bid limit for you. Once you have pre-registered for a live online auction, you can see your intended spend and bid limit by going to 'Account Settings' and clicking on 'Live Bidding Registrations'.
Your bid limit will be the maximum amount you can bid during the auction. Your bid limit is for the hammer price and is not affected by the buyer’s premium and VAT. For example, if you have a bid limit of €1,000 and place two winning bids for €300 and €200, then you will only be able to bid €500 for the rest of the auction. If you try to place a bid that is higher than €500, you will not be able to do so.
Online Absentee and Telephone Bids
You can now leave absentee and telephone bids on our website!
Absentee Bidding
Once you've created an account and your identity is verified, you can leave your absentee bid directly on the lot page. We will contact you when your bids have been confirmed.
Telephone Bidding
Once you've created an account and your identity is verified, you can leave telephone bids online. We will contact you when your bids have been confirmed.
Classic Absentee and Telephone Bidding Form
You can still submit absentee and telephone bids by email or fax if you prefer. Simply fill out the Absentee Bidding/Telephone bidding form and return it to us by email at office@zacke.at or by fax at +43 (1) 532 04 52 20. You can download the PDF from our Upcoming Auctions page.
How-To Guides
How to Create Your Personal Zacke Account
How to Register to Bid on Zacke Live
How to Leave Absentee Bids Online
How to Leave Telephone Bids Online
中文版本的操作指南
创建新账号
注册Zacke Live在线直播竞拍(免平台费)
缺席投标和电话投标
Third-Party Bidding
We partner with best-in-class third-party partners to make it easy for you to bid online in the channel of your choice. Please note that if you bid with one of our third-party online partners, then there will be a live bidding surcharge on top of your final purchase price. You can find all of our fees here. Here's a full list of our third-party partners:
- 51 Bid Live
- EpaiLive
- ArtFoxLive
- Invaluable
- LiveAuctioneers
- the-saleroom
- lot-tissimo
- Drouot
Please note that we place different auctions on different platforms. For example, in general, we only place Chinese art auctions on 51 Bid Live.
Bidding in Person
You must register to bid in person and will be assigned a paddle at the auction. Please contact us at office@zacke.at or +43 (1) 532 04 52 for the latest local health and safety guidelines.