11th Mar, 2022 10:00
DAY 2 - TWO-DAY AUCTION - Fine Chinese Art / 中國藝術集珍 / Buddhism & Hinduism
558
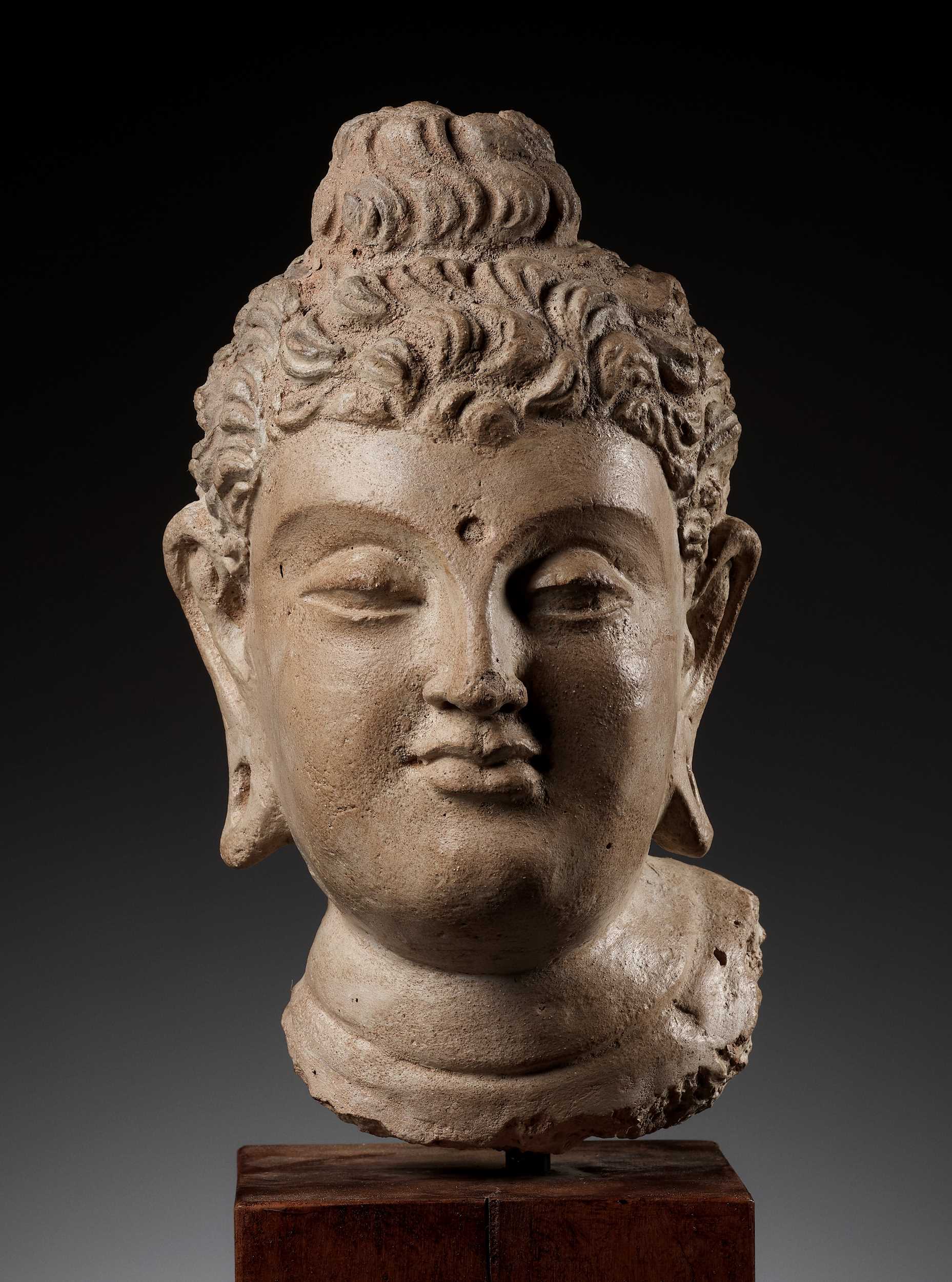
A RARE AND IMPORTANT TERRACOTTA HEAD OF BUDDHA SHAKYAMUNI
罕見重要陶土釋迦牟尼頭像
Sold for €11,376
including Buyer's Premium
Ancient region of Gandhara, Kushan period, 4th-5th century. The large head is superbly modeled with a serene and meditative expression, with almond-shaped eyes below gently arched brows, distinct recessed urna, aquiline nose, and full lips forming a calm, benevolent smile. The wavy hair is surmounted by a domed ushnisha.
Scientific Analysis Report: A Thermoluminescence sample analysis has been conducted by Oxford Authentication, TL test no. N116n7, dated 18 October 2016, and is consistent with the suggested period of manufacture, a copy of the thermoluminescence analysis report accompanies this lot (the original is lost).
Provenance: Arthur Huc (1854-1932). Marcel Huc, inherited from the above. Thence by descent within the same family. Arthur Huc was the chief editor of La Dépêche du Midi, at the time the leading newspaper in Toulouse, France. He was also an accomplished art critic and early patron of several artists, including Henri de Toulouse- Lautrec. At the same time, Arthur Huc was a keen collector of Asian art, a passion that he inherited from his legendary ancestor Évariste Régis Huc, also known as the Abbé Huc (1813-1860), a French Catholic priest and traveler who became famous for his accounts of Qing-era China, Mongolia and especially the then-almost-unknown Tibet in his book “Remembrances of a Journey in Tartary, Tibet, and China”.
Inventory List: In 1954, L. Magniette, bailiff of the court in Toulouse (Huissier), was ordered to compile a complete inventory of the collection inherited by Marcel Huc from his father, Arthur Huc, the so-called “Inventaire Huc”. The present lot is listed in this inventory as follows: “Serie de vingt deux têtes en terre-cuite. GANDHARA” (series of twenty-two terracotta heads. GANDHARA). A copy of the inventory list and cover page are accompanying this lot.
Condition: Very good condition, commensurate with dating and presenting magnificently overall. Some wear and firing flaws, minor nicks, shallow cracks, losses to exposed areas, all hardly noticeable due to a light-colored varnish coating which was applied a long time ago. Overall, fully consistent with the high age of this sculpture.
French Export License: Certificat d’exportation pour un bien culturel Nr. 185425 dated 3 July 2017 has been granted and is accompanying this lot.
Weight: 7.9 kg (excl. stand)
Dimensions: Height 34 cm (excl. stand) and 55 cm (incl. stand)
Mounted on an old associated hardwood stand. (2)
The kingdom of Gandhara lasted from 530 BC to 1021 AD, when its last king was murdered by his own troops. It stretched across parts of present-day Afghanistan and Pakistan. Gandhara is noted for its distinctive style in Buddhist art, which developed out of a merger of Greek, Syrian, Persian and Indian artistic influence. Gandharan style flourished and achieved its peak during the Kushan period, from the 1st to the 5th century. In the first century AD, Gandhara was the birthplace of some of the earliest Buddhist images.
The use of hard-fired ceramic instead of stone such as schist became popular during the later Gandharan period from the 4th to 6th centuries AD. Fired clay was expensive in the area, because the wood needed for the firing process was scarce. Therefore, such an expensive sculpture would have been a highly meritorious Buddhist offering. Only a few terracotta statues from this period and of this size have ever been recorded.
The masterfully carved head of Buddha is a fine example of the rich cultural interplay and hybrid art styles of the Gandharan empire in the first centuries CE and embodies an idealized, transcendent male form of an earthly prince. Based on Greco-Roman prototypes, his elegant neck is slightly elongated, and his heavy eyelids frame a pair of almond-shaped eyes, his forehead remaining perfectly uncreased, and there is no tension in his rosebud mouth. While activated with energy, movement and life, the Buddha is simultaneously in a state of otherworldly tranquility.
The sculptor has also skillfully referenced Buddha’s earlier history as Prince Siddhartha by placing rounded recesses in the elongated earlobes where, as a prince, he would have worn heavy jewelry. This detail reminds the viewer that, while the Prince’s past was centered on excess, the absence of material goods – jewelry and fine clothing – emphasizes the Buddha’s renunciation of worldly attachments.
Compare the face of this Buddha with that of another in the Peshawar Museum (see H. Ingholt, Gandharan Art in Pakistan, 1957, p.113, fig.223). In both examples, the artist has skillfully carved and polished the face to transform it into human skin. While the face of the published image bears a rather formulaic manner, the present work has been carved by a master of naturalism. The softly rounded cheeks give way to hollows on either side, the upper and lower lids are nearly spherical to emphasize the eyes, and the pupils are not carved. The quiet contours and gentle shadows model the flawless structure of the face, encapsulating the eternal youthfulness of the Buddha. Almost androgynous in appearance, the Buddha transcends gender, embodying the perfect balance of masculinity and femininity.
Expert’s note: This head has a high aesthetic value, illustrious provenance, and is in a beautifully preserved condition. It is an important and rare masterpiece of Gandharan art.
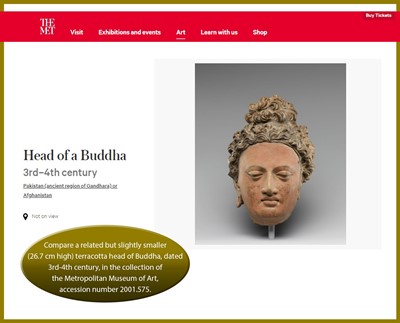
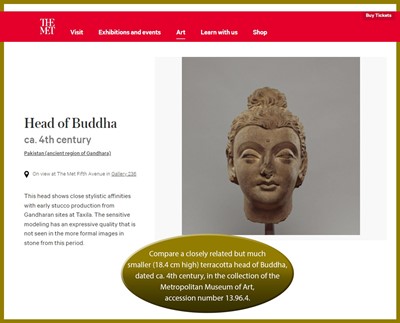
Literature comparison: Compare a related but slightly smaller (26.7 cm high) terracotta head of Buddha, dated 3rd-4th century, in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, accession number 2001.575. Compare a closely related but much smaller (18.4 cm high) terracotta head of Buddha, dated ca. 4th century, in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, accession number 13.96.4.
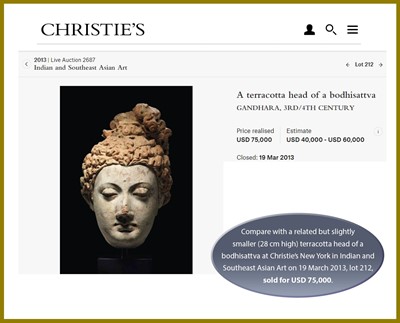
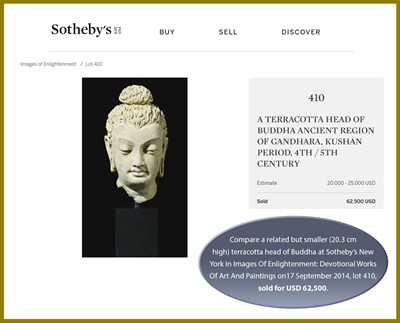
Auction result comparison: Compare with a related but slightly smaller (28 cm high) terracotta head of a bodhisattva at Christie’s New York in Indian and Southeast Asian Art on 19 March 2013, lot 212, sold for USD 75,000. Compare a related but smaller (20.3 cm high) terracotta head of Buddha at Sotheby’s New York in Images Of Enlightenment: Devotional Works Of Art And Paintings on 17 September 2014, lot 410, sold for USD 62,500.
罕見重要陶土釋迦牟尼頭像
健陀羅,四至五世紀。大型佛頭造型優美,沉靜冥思,眉毛下方拱形杏仁狀眼睛,眉間白毫,豐滿的鼻子,溫柔仁慈的笑容。頭髮緊卷,呈螺髻。
科學檢測報告:隨附一份牛津熱釋光檢測鑒定報告(原件遺失)。監測報告 no. N116n7,2016年10月18日,與目前斷代一致。
來源:Arthur Huc (1854-1932)收藏。 Marcel Huc繼承,自此保存在同一家族至今。 Arthur Huc是La Dépêchedu Midi的主編,這是當時法國圖盧茲的主要報紙。他還是一位出色的藝術評論家,也是包括Henri de Toulouse- Lautrec在內的幾位藝術家的早期贊助人。同時,Arthur Huc是一位熱衷於亞洲藝術的收藏家,他的熱情源於他的傳奇祖先Évariste Régis Huc,中文名為古伯察(1813-1860),是法國天主教神父和旅行作家,在他的《韃靼西藏旅行記》書中描述了他在清朝、以及蒙古的遊歷,尤其是當時幾乎鮮為人知的西藏。
收藏清單:1954年,圖盧茲法院法警 L. Magniette奉命對Marcel Huc從其父親Arthur Huc繼承的收藏品進行完整目錄彙編,即所謂的“ Inventaire Huc”。此拍品也在當時列出的收藏清單中“ Serie de vingt deuxtêtesen terre-cuite。 GANDHARA”(二十二個陶土頭像系列,健陀羅)。隨附清單和封面副本。
品相:狀況很好,尤其是考慮到這件作品的年代。一些燒製瑕疵,輕微的刻痕和凹痕,裸露區域有材料缺損。表面的清漆應爲很久之前所塗,所以現在已經基本看不出來了。總體而言,狀況與該雕塑的年代相符。
法國出口證書: 隨附法國2017年7月3日出具的出口證書Certificat d’exportation pour un bien culturel Nr. 185425。
重量: 7.9 公斤 (不含底座)
尺寸: 高 34 厘米 (不含底座),總 55 厘米
硬木底座 (2)
拍賣結果比較: 一件相近但稍小 (28 厘米) 陶土菩薩頭像,見紐約佳士得Indian and Southeast Asian Art拍場2013年3月19日 lot 212, 售價USD 75,000;一件相近但更小 (20.3 厘米) 的佛陀陶土頭像,見紐約蘇富比Images Of Enlightenment: Devotional Works Of Art And Paintings拍場2014年9月17日 lot 410, 售價USD 62,500。
Ancient region of Gandhara, Kushan period, 4th-5th century. The large head is superbly modeled with a serene and meditative expression, with almond-shaped eyes below gently arched brows, distinct recessed urna, aquiline nose, and full lips forming a calm, benevolent smile. The wavy hair is surmounted by a domed ushnisha.
Scientific Analysis Report: A Thermoluminescence sample analysis has been conducted by Oxford Authentication, TL test no. N116n7, dated 18 October 2016, and is consistent with the suggested period of manufacture, a copy of the thermoluminescence analysis report accompanies this lot (the original is lost).
Provenance: Arthur Huc (1854-1932). Marcel Huc, inherited from the above. Thence by descent within the same family. Arthur Huc was the chief editor of La Dépêche du Midi, at the time the leading newspaper in Toulouse, France. He was also an accomplished art critic and early patron of several artists, including Henri de Toulouse- Lautrec. At the same time, Arthur Huc was a keen collector of Asian art, a passion that he inherited from his legendary ancestor Évariste Régis Huc, also known as the Abbé Huc (1813-1860), a French Catholic priest and traveler who became famous for his accounts of Qing-era China, Mongolia and especially the then-almost-unknown Tibet in his book “Remembrances of a Journey in Tartary, Tibet, and China”.
Inventory List: In 1954, L. Magniette, bailiff of the court in Toulouse (Huissier), was ordered to compile a complete inventory of the collection inherited by Marcel Huc from his father, Arthur Huc, the so-called “Inventaire Huc”. The present lot is listed in this inventory as follows: “Serie de vingt deux têtes en terre-cuite. GANDHARA” (series of twenty-two terracotta heads. GANDHARA). A copy of the inventory list and cover page are accompanying this lot.
Condition: Very good condition, commensurate with dating and presenting magnificently overall. Some wear and firing flaws, minor nicks, shallow cracks, losses to exposed areas, all hardly noticeable due to a light-colored varnish coating which was applied a long time ago. Overall, fully consistent with the high age of this sculpture.
French Export License: Certificat d’exportation pour un bien culturel Nr. 185425 dated 3 July 2017 has been granted and is accompanying this lot.
Weight: 7.9 kg (excl. stand)
Dimensions: Height 34 cm (excl. stand) and 55 cm (incl. stand)
Mounted on an old associated hardwood stand. (2)
The kingdom of Gandhara lasted from 530 BC to 1021 AD, when its last king was murdered by his own troops. It stretched across parts of present-day Afghanistan and Pakistan. Gandhara is noted for its distinctive style in Buddhist art, which developed out of a merger of Greek, Syrian, Persian and Indian artistic influence. Gandharan style flourished and achieved its peak during the Kushan period, from the 1st to the 5th century. In the first century AD, Gandhara was the birthplace of some of the earliest Buddhist images.
The use of hard-fired ceramic instead of stone such as schist became popular during the later Gandharan period from the 4th to 6th centuries AD. Fired clay was expensive in the area, because the wood needed for the firing process was scarce. Therefore, such an expensive sculpture would have been a highly meritorious Buddhist offering. Only a few terracotta statues from this period and of this size have ever been recorded.
The masterfully carved head of Buddha is a fine example of the rich cultural interplay and hybrid art styles of the Gandharan empire in the first centuries CE and embodies an idealized, transcendent male form of an earthly prince. Based on Greco-Roman prototypes, his elegant neck is slightly elongated, and his heavy eyelids frame a pair of almond-shaped eyes, his forehead remaining perfectly uncreased, and there is no tension in his rosebud mouth. While activated with energy, movement and life, the Buddha is simultaneously in a state of otherworldly tranquility.
The sculptor has also skillfully referenced Buddha’s earlier history as Prince Siddhartha by placing rounded recesses in the elongated earlobes where, as a prince, he would have worn heavy jewelry. This detail reminds the viewer that, while the Prince’s past was centered on excess, the absence of material goods – jewelry and fine clothing – emphasizes the Buddha’s renunciation of worldly attachments.
Compare the face of this Buddha with that of another in the Peshawar Museum (see H. Ingholt, Gandharan Art in Pakistan, 1957, p.113, fig.223). In both examples, the artist has skillfully carved and polished the face to transform it into human skin. While the face of the published image bears a rather formulaic manner, the present work has been carved by a master of naturalism. The softly rounded cheeks give way to hollows on either side, the upper and lower lids are nearly spherical to emphasize the eyes, and the pupils are not carved. The quiet contours and gentle shadows model the flawless structure of the face, encapsulating the eternal youthfulness of the Buddha. Almost androgynous in appearance, the Buddha transcends gender, embodying the perfect balance of masculinity and femininity.
Expert’s note: This head has a high aesthetic value, illustrious provenance, and is in a beautifully preserved condition. It is an important and rare masterpiece of Gandharan art.
Literature comparison: Compare a related but slightly smaller (26.7 cm high) terracotta head of Buddha, dated 3rd-4th century, in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, accession number 2001.575. Compare a closely related but much smaller (18.4 cm high) terracotta head of Buddha, dated ca. 4th century, in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, accession number 13.96.4.
Auction result comparison: Compare with a related but slightly smaller (28 cm high) terracotta head of a bodhisattva at Christie’s New York in Indian and Southeast Asian Art on 19 March 2013, lot 212, sold for USD 75,000. Compare a related but smaller (20.3 cm high) terracotta head of Buddha at Sotheby’s New York in Images Of Enlightenment: Devotional Works Of Art And Paintings on 17 September 2014, lot 410, sold for USD 62,500.
罕見重要陶土釋迦牟尼頭像
健陀羅,四至五世紀。大型佛頭造型優美,沉靜冥思,眉毛下方拱形杏仁狀眼睛,眉間白毫,豐滿的鼻子,溫柔仁慈的笑容。頭髮緊卷,呈螺髻。
科學檢測報告:隨附一份牛津熱釋光檢測鑒定報告(原件遺失)。監測報告 no. N116n7,2016年10月18日,與目前斷代一致。
來源:Arthur Huc (1854-1932)收藏。 Marcel Huc繼承,自此保存在同一家族至今。 Arthur Huc是La Dépêchedu Midi的主編,這是當時法國圖盧茲的主要報紙。他還是一位出色的藝術評論家,也是包括Henri de Toulouse- Lautrec在內的幾位藝術家的早期贊助人。同時,Arthur Huc是一位熱衷於亞洲藝術的收藏家,他的熱情源於他的傳奇祖先Évariste Régis Huc,中文名為古伯察(1813-1860),是法國天主教神父和旅行作家,在他的《韃靼西藏旅行記》書中描述了他在清朝、以及蒙古的遊歷,尤其是當時幾乎鮮為人知的西藏。
收藏清單:1954年,圖盧茲法院法警 L. Magniette奉命對Marcel Huc從其父親Arthur Huc繼承的收藏品進行完整目錄彙編,即所謂的“ Inventaire Huc”。此拍品也在當時列出的收藏清單中“ Serie de vingt deuxtêtesen terre-cuite。 GANDHARA”(二十二個陶土頭像系列,健陀羅)。隨附清單和封面副本。
品相:狀況很好,尤其是考慮到這件作品的年代。一些燒製瑕疵,輕微的刻痕和凹痕,裸露區域有材料缺損。表面的清漆應爲很久之前所塗,所以現在已經基本看不出來了。總體而言,狀況與該雕塑的年代相符。
法國出口證書: 隨附法國2017年7月3日出具的出口證書Certificat d’exportation pour un bien culturel Nr. 185425。
重量: 7.9 公斤 (不含底座)
尺寸: 高 34 厘米 (不含底座),總 55 厘米
硬木底座 (2)
拍賣結果比較: 一件相近但稍小 (28 厘米) 陶土菩薩頭像,見紐約佳士得Indian and Southeast Asian Art拍場2013年3月19日 lot 212, 售價USD 75,000;一件相近但更小 (20.3 厘米) 的佛陀陶土頭像,見紐約蘇富比Images Of Enlightenment: Devotional Works Of Art And Paintings拍場2014年9月17日 lot 410, 售價USD 62,500。
Zacke Live Online Bidding
Our online bidding platform makes it easier than ever to bid in our auctions! When you bid through our website, you can take advantage of our premium buyer's terms without incurring any additional online bidding surcharges.
To bid live online, you'll need to create an online account. Once your account is created and your identity is verified, you can register to bid in an auction up to 12 hours before the auction begins.
Intended Spend and Bid Limits
When you register to bid in an online auction, you will need to share your intended maximum spending budget for the auction. We will then review your intended spend and set a bid limit for you. Once you have pre-registered for a live online auction, you can see your intended spend and bid limit by going to 'Account Settings' and clicking on 'Live Bidding Registrations'.
Your bid limit will be the maximum amount you can bid during the auction. Your bid limit is for the hammer price and is not affected by the buyer’s premium and VAT. For example, if you have a bid limit of €1,000 and place two winning bids for €300 and €200, then you will only be able to bid €500 for the rest of the auction. If you try to place a bid that is higher than €500, you will not be able to do so.
Online Absentee and Telephone Bids
You can now leave absentee and telephone bids on our website!
Absentee Bidding
Once you've created an account and your identity is verified, you can leave your absentee bid directly on the lot page. We will contact you when your bids have been confirmed.
Telephone Bidding
Once you've created an account and your identity is verified, you can leave telephone bids online. We will contact you when your bids have been confirmed.
Classic Absentee and Telephone Bidding Form
You can still submit absentee and telephone bids by email or fax if you prefer. Simply fill out the Absentee Bidding/Telephone bidding form and return it to us by email at office@zacke.at or by fax at +43 (1) 532 04 52 20. You can download the PDF from our Upcoming Auctions page.
How-To Guides
How to Create Your Personal Zacke Account
How to Register to Bid on Zacke Live
How to Leave Absentee Bids Online
How to Leave Telephone Bids Online
中文版本的操作指南
创建新账号
注册Zacke Live在线直播竞拍(免平台费)
缺席投标和电话投标
Third-Party Bidding
We partner with best-in-class third-party partners to make it easy for you to bid online in the channel of your choice. Please note that if you bid with one of our third-party online partners, then there will be a live bidding surcharge on top of your final purchase price. You can find all of our fees here. Here's a full list of our third-party partners:
- 51 Bid Live
- EpaiLive
- ArtFoxLive
- Invaluable
- LiveAuctioneers
- the-saleroom
- lot-tissimo
- Drouot
Please note that we place different auctions on different platforms. For example, in general, we only place Chinese art auctions on 51 Bid Live.
Bidding in Person
You must register to bid in person and will be assigned a paddle at the auction. Please contact us at office@zacke.at or +43 (1) 532 04 52 for the latest local health and safety guidelines.